Resource-Efficient Personal Large Language Models Fine-Tuning with Collaborative Edge Computing
Shengyuan Ye,
Bei Ouyang,
Tianyi Qian,
Liekang Zeng,
Jingyi Li,
Jiangsu Du,
Xiaowen Chu,
Guoliang Xing,
Xu Chen
January 2026
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) have unlocked a plethora of powerful applications at the network edge, such as intelligent personal assistants. Data privacy and security concerns have prompted a shift towards edge-based fine-tuning of personal LLMs, away from cloud reliance. However, this raises issues of computational intensity and resource scarcity, hindering training efficiency and feasibility. While current studies investigate parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) techniques to mitigate resource constraints, our analysis indicates that these techniques are not sufficiently resource-efficient for edge devices. Other studies focus on exploiting the potential of edge devices through resource management optimization, yet are ultimately bottlenecked by the resource wall of individual devices. To tackle these challenges, we propose PAC+, a resource efficient collaborative edge AI framework for in-situ personal LLMs fine-tuning. PAC+ breaks the resource wall of personal LLMs fine-tuning with a sophisticated algorithm-system codesign. (1) Algorithmically, PAC+ implements a personal LLMs fine-tuning technique that is efficient in terms of parameters, time, and memory. It utilizes Parallel Adapters to circumvent the need for a full backward pass through the LLM backbone. Additionally, an activation cache mechanism further streamlining the process by negating the necessity for repeated forward passes across multiple epochs. (2) Systematically, PAC+ leverages edge devices in close proximity, pooling them as a collective resource for in-situ personal LLMs fine-tuning, utilizing a hybrid data and pipeline parallelism to orchestrate distributed training. The use of the activation cache eliminates the need for forward pass through the LLM backbone, enabling exclusive fine-tuning of the Parallel Adapters using data parallelism. Extensive evaluation of the prototype implementation demonstrates that PAC+ significantly outperforms existing collaborative edge training systems, achieving up to a 9.7× end-to-end speedup. Furthermore, compared to mainstream LLM fine-tuning algorithms, PAC+ reduces memory footprint by up to 88.16%.
Publication
IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems (IEEE TPDS), 2026.

Shengyuan Ye
Ph.D. student at SMCLab
He is a Ph.D. student at School of Computer Science and Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University. His research interests include Resource-efficient AI Systems and Applications with Mobile AI.

Liekang Zeng
Ph.D., Sun Yat-sen University
He obtained Ph.D. degree at School of Computer Science and Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University. His research interest lies in building edge intelligence systems with real-time responsiveness, systematic resource efficiency, and theoretical performance guarantee.

Jiangsu Du
Assistant Professor, Sun Yat-sen University
He obtained Ph.D. degree at School of Computer Science and Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University. He is now a Assistant Professor at the Sun Yat-sen University, working on High Performance Computing, and Distributed Artificial Intelligence System.

Xiaowen Chu
Professor, HKUST(GZ)
Acting Head, Data Science and Analytics Thrust
Dr. Chu is currently a Professor at the Data Science and Analytics Thrust, Information Hub of HKUST(GZ), and an Affiliate Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, HKUST. His current research interests include GPU Computing, Distributed Machine Learning, Cloud Computing, and Wireless Networks. He is especially interested in the modelling, parallel algorithm design, application optimization, and energy efficiency of GPU computing.

Guoliang Xing
Professor, IEEE Fellow, CUHK
Director, CUHK AIoT Lab
Professor Xing’s research lies at the intersection between systems, embedded AI, algorithms, and physical domains including health, autonomous driving, and environment. His research group develops new technologies at the frontier of mobile health, autonomous driving, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), Internet of Things (IoT), wireless networks, security and privacy.

Xu Chen
Professor and Assistant Dean, Sun Yat-sen University
Director, Institute of Advanced Networking & Computing Systems
Xu Chen is a Full Professor with Sun Yat-sen University, Director of Institute of Advanced Networking and Computing Systems (IANCS), and the Vice Director of National Engineering Research Laboratory of Digital Homes. His research interest includes edge computing and cloud computing, federated learning, cloud-native intelligent robots, distributed artificial intelligence, intelligent big data analysis, and computing power network.
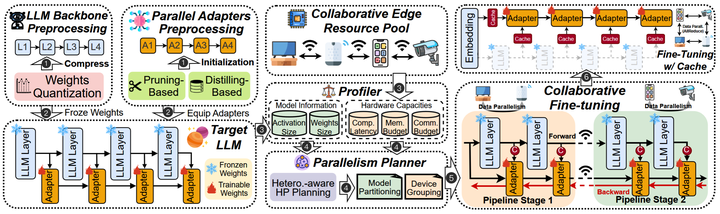 PAC+ Overview
PAC+ Overview